TC03 - ICT tools in education (ÁTNÉZNI!: sok link és icon rossz/hiányzik)
E-learning curriculum
 Learning objectives
Learning objectives
When you have completed this session, you should be able to
- define term "synopsis",
- create one of the most important documents in planning an e-curriculum.
Synopsis
Drawing up the synopsis is the fir st step of curriculum development. The synopsis (comes from the Greek synopsesthai – means see together) the same scenario is used in film production, a brief summary of the act of the film. Today's meaning is: overview, summary, abstract, content, bulky writing content outline. In relation to electronic curriculum development: Short but comprehensive presentation of all material of the curriculum, defines the approximately estimated development costs, and transparency over the development concept.
st step of curriculum development. The synopsis (comes from the Greek synopsesthai – means see together) the same scenario is used in film production, a brief summary of the act of the film. Today's meaning is: overview, summary, abstract, content, bulky writing content outline. In relation to electronic curriculum development: Short but comprehensive presentation of all material of the curriculum, defines the approximately estimated development costs, and transparency over the development concept.
Appropriate for teachers to show their didactic objectives, verify that the digital learning materials for the selected target groups offers more (as compared to traditional methods)
For example we would like to win support for proposals for electronic curriculum development. Based on the synopsis the evaluators can decide that the proposed expenditures are in accordance with the expected results.
Synopsis structure
1. Objectives, define topics
At this point the teacher sets out: the subject, within a topic, the age of the group to produce electronic curriculum, and the purpose of development.
The content outline contains minimum the followings:
a. objective, target group (ages)
b. subject
c. topic
d. „sub” topic
It’s proposed to choose such a unit from the topic, which is difficult to teach with traditional methods and using a computer is justified in methodological and didactic point of view, where interactive elements could help understanding and learning. For example learning new words in a foreign language or topic of transformations of the function in mathematica.
2. The number and size of learning units
Learning unit is a part of the e-learning phase which can learn in (20-40 minutes). The synopsis should describe how many learning units needed for the topic and measure the extent of text material.The standard unit of measurement of schoolbook writing is an “author sheet”, it means 16 A4 pages, with an A4 page 25 rows and 60 characters per line (1500) included.
|
Learning unit |
Short content |
Size |
|
1. |
For the content summary of each course it's required to estimate the number of the
a. sample tasks,
b. practising tasks,
c. test,
(with keys),
d. concept definition
|
Learing unit |
Number of exercises |
|||
|
sample task |
practising task |
test |
definition |
|
|
1. |
||||
|
2. |
||||
|
... |
||||
|
all |
||||
The table provides information to estimate the necessary work. The requirements of interactive, and multimedia based tasks (programming, design, editing) are in the next block the following synopsis.Summary, in the second part of the synopsis we plan the required author’s work, text learning objects content and their number.
3. Pedagigical methods
 In this section we write shortly about our pedagogical and didactical concept such as:
In this section we write shortly about our pedagogical and didactical concept such as:
- Is this learning unit for individual learning or for practising
- Frontal or group learning
- How to apply them
- How can others use this finished material
- How to control and evaluate the acquired knowledge
- How to build the digital unit to the educational process
- Prove a methodological summary we have a pedagogical thought outline, our concept is complete the development is not for itself
|
Methodological outline |
||
|
Learning unit |
processing method (proposed time of period) |
Method of control and evaluation |
|
1. |
||
Examples:
a, Within a subject for some special topic the lesson is in the computer lab. During the digital lesson the students under the teacher’s supervision process the learning material on their own.
b, Use a presentation system ( projector, laptop) in the classroom and work in frontal or in groups.
c, Use the electronic unit in addition for their classroom lessons, to practise, control them after their lessons.
d, Our students write closing theme test in the computer lab. The system store the results for the teacher and shows for the students immediately.
e, If we public the curriculum on CD, students can take it home.
These possibilities can be combined.
Note: Not necessary to use a table form!
4. Learning Objects
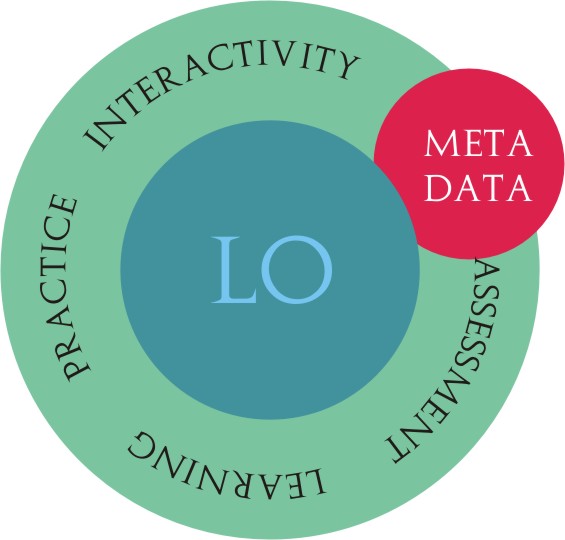 In the high-quality e-learning material development the significant part of costs comes from designing and planning media elements. In the synopsis it is required to define the type (picture, sound, video) and number of the LO-s in the unit.
In the high-quality e-learning material development the significant part of costs comes from designing and planning media elements. In the synopsis it is required to define the type (picture, sound, video) and number of the LO-s in the unit.
It can cause serious problem if the plan and the resource estimating is not accurate, because during the process probably external expert work will be needed. Based on the synopsis the external orders must be prepared. Particularly dangerous to underestimate the potential of IT and graphic design work, because in this case is forced to decrease the construction cost (at the expense of quality) or take on the additional work, which is not covered with the low calculated costs. If the media objects are not prepared for yourself, you should ask for a bid from an expert.
The quantification is possible in a simple table, if we have approximately the same quality (same size) images, if the images and animations are simple, and the length of the sounds and videos are similar. In this case you also need to attach an explanation about the length of the sounds, and their type (narration, music or actor’s narration).
|
Learning unit number
|
graphic (digital drawing) |
Digitized image |
Animation |
Video |
Sound |
Interactive elements
|
|
1. |
2 |
3 |
1 |
0 |
3 |
10 |
|
2. |
||||||
|
... |
||||||
|
All |
In the column of interactive elements think of programming work required elements (for example, test exercise with animation or puzzle with graphic elements or matching tasks. In multimedia systems (e.g. flash) small programmes (scripts) ensure interactions, checking the solutions and evaluation.
For planning real costs further additions are needed for the table if we plan a more difficult 3D simulation animation, or a small film clip work out in a film studio. Always ask for a specific bid to avoid to under or overestimate the costs.
5. Format of media elements, software and hardware requirements for the production
Format of media elements, software and hardware requirements for the production
Very important to use standard digital formats, fit to several frame systems. Consult an IT expert to choose the required software and hardware for the production. It’s very useful if we would like to sell our end product. Look around to find some free software or calculate their costs.
|
media element |
format |
software |
hardware |
|
photo |
JPG |
digital camera |
|
| graphic | |||
|
narration |
|||
|
… |
6. Source, copyright information
The source should be listed rely on your curriculum like bibliography in books. Always keep up the copyright laws and if needed ask permission from the author.
If you want to sell your electronic curriculum, maybe you have to pay some royalty for some elements. Not forget to calculate with them and keep up the royalties in advance.
7. Publication
Write here about the software and hardware environment of your curriculum. The selected framework specifies the format of the LO-s should be prepared (e.g. image size due to transfer limit). For example for CD-s with a well-known software, or for an open source system on the Internet or both of them.
8. Notes
1. Take care the synpnopsis not to bee very large, but contains all the essential elements needed for the evalution of the concept.
2. It is possible you need some modification during the implementation so it's worth calculating with some margin (max. ±10%) .
Bibliography:
[1] Tay Vaughan: Multimedia, Osborn McGraw-Hill, Berkely, 1999.
[2] Rakaczkiné, dr Tóth K., Szabó J., Szentpétery Zsolt: Az e-tenanyag fejlesztésének pedagógiai-távoktatási alapjai, SZIE, GTK Közép-Magyarországi Regionális Távoktatási Központ, Gödöllő, 2002.