TC03 - ICT tools in education (ÁTNÉZNI!: sok link és icon rossz/hiányzik)
E-learning curriculum
Planning and Implementation
 Learning objectives
Learning objectives
When you have completed this session, you should be able to
- plan an e-learning curriculum.
Planning and implementation
A multimedia curriculum is complex with a number of development projects. Key stages:
|
Project preapring |
Analisys: needs, objectives |
|
Content, pedagogical, methodical planning – synopsis |
|
|
Feasibility study: spending plans, schedules |
|
|
Project start |
Project establishment, distribution of tasks, deadlines, responsibilities |
|
Content design |
write curriculum, proofreading |
|
Preparing graphic plans |
Preparing graphics – design elements |
|
Storyboard |
|
|
Implementation |
media elements |
|
LO-s integration, collating |
|
|
Documentation |
|
|
Testing, modification |
|
|
E-method proofreading, evaluation, modofication |
|
|
master preparation, documentation, archiving |
|
|
Project end |
Final reports, project evaluation and project closure |
Watch this video!
 |
1. Analysis
- First of all you have to considered with the following:
- Learning environment
- Pedagogical objectives
- Available tools, equipment
- Sources
- Pedagogical programme of the school
2. Content, pedagogical and method planning
In this section you should be demolished the development general objectives to learning unit level. Formulate specific objectives, requirements, building of the unit for "screen".
E-curriculum sturcture
|
Topic |
|
"sub"topic |
|
Learning unit |
|
LO-s · Text · media elements (image, sound, movie) · animation (pl. flash) |
Learning unit structure
The learning units have been designed to the student in a learning stage - without a break - not more than 20-40 minutes for self-learning or teach them.
Learning unit elements:
1) Introduction: : a brief, one or two sentences to describes the specific topic
2) Motivation: the student's motivation (for example, introduction to the benefits of this new knowledge
3) Description: : The new skills
4) Practising: tests, simulations or other interactive elements
5) Summary: a brief summary of the topic
Synopsis
Synopsis is a short but comprehensive presentation of all material of the curriculum, defines the approximately estimated development costs, and transparency over the development concept.
Appropriate for teachers to show their didactic objectives, verify that the digital learning materials for the selected target groups offers more (as compared to traditional methods). This documnet is the first step in e-learning development.
3. Writing curriculum, proofreading
In the third phase starts the professional content work, writing the curriculum, and preparation of assessment materials. Authors and assistants working together the finished curriculum is assessed by professional, linguistic and methodological assistants. It's different from the traditional curriculum writing despite the many similarities. Don't forget to think of screen-sized units.
4. Preparing graphics – design elements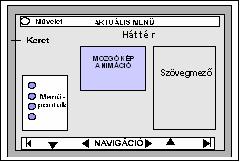
Design is an important element of an electronic curriculum. You decided that the texts will be readable or not the graphics, images, illustrations truly serve the desired effect or, conversely, the mediaelements distract the learner's attention from the essence.
5. Storyboard
Storyboard is one of the most important step in planning. In this work phase you should define the final design, content, function elements.
|
Storyboard comes from film industry, which describes the production in small details. ( screen) The storyboard is based on the synopsis, but while the first synopsis of the content and teaching focuses on the objective, while the storyboard is for the implementation of technical manual. |
Based on the storyboard (graphic designers, programmers) step-by-step can be made the production without any further instruction.
6. Preparing, editing media elements
In this work phase carried out the necessary graphics, digitizing images, narrations, music, sound, video etc.) The quality of the media elements is very important.
An important element of the period of work is programming, because the interactive elements (tests, exercises, simulations) required for programming work.
During the preparation and collection of media elements, not forget the copyright issues!
7. Implementation, LO-s integration, documentation
Building the electronic learning material, follows the instructions of the storyboard in a software development environment or frame system. It's called implementation. Integration - depending on the environment - often requires programming work, and in the final work phase maybe "fine tuning" is needed. Fine tuning means to synchronize the media objects with each other.
Required from the programers (if its even yourself!)to document the source code for the subsequent amendments. At the end of the improvements it's important to make the product documentation.
8. Testing, e-method proofreading
Testing is an important phase. All your efforts above are of little value if the product is notaccessible and usable. Consideration of usability factors actually begins in the planning phase but it should be formally tested during prototyping, then following full production. The importance of testing and considering the usability factors cannot be over-stressed.
These steps require:
• Knowing what standards should be aimed for (technical compliance and
usability of the product being developed).
• Establishing means by which to measure or test that standards and usability
objective have been achieved.
• Considering when to measure, and how information from this will feed back
into the development process to achieve best outcomes most efficiently.
9. Master preparation, archiving
Latest you should archive all the sources for safety reasons and for subsequent amendments.
Master copy is always be prepared, regardless of whether the product is a CD-ROM, DVD, or publish it on the Internet for reproduction, later re-using.
If we use an integrated frame system archiving (regular backups) is automatical, but it's important to preserve the sources.
Finally…
The chapter is about professional development. If the development is well-prepared, the result is not be the all work of employees, it could be a effective product.
Bibliography:
[1] Tay Vaughan: Multimedia, Osborn McGraw-Hill, Berkely, 1999. Hazai kiadás: Panem Könyvkiadó, Budapest, 2002.
[2] Rakaczkiné, dr Tóth K., Szabó J., Szentpétery Zsolt: Az e-tenanyag fejlesztésének pedagógiai-távoktatási alapjai, SZIE, GTK Közép-Magyarországi Regionális Távoktatási Központ, Gödöllő, 2002.
[3] Hutter O., Magyar G., Mlinarics J.: E-learning 2005, Műszaki Könyvkiadó, Budapest, 2005.
[4] Kovács Ilma: Az elektronikus tanulásról, Holnap Kiadó, 2007